| About Entities | 
|
 | About Entities | 
|
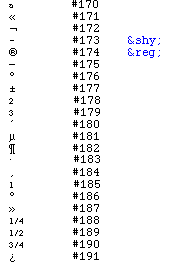
The original HTML-language does not allow special characters other than the usual ones in the English language. To write a Swedish å, ä or ö, to write accents of e and other characters or to insert symbols like $ and ©, there are so called entities. An entity begins with an ampersand and ends with a semicolon, and in between, there are usually the character that is enhanced followed by a few more letters that indicates how it would appear. For example, é means é. An entity can also be written using "&#" followed by the character value and finally a semicolon.
The standard used to define entities is called ISO Latin-1. Today, many pages do have special characters anyway, since most browsers will understand them. If you're not using entities, you should include <META HTTP-EQUIV="Content-Type" CONTENT="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1"> in the head-section of your page.
Special Characters
There are a few characters that must be coded in different ways since they are otherwise
used to define HTML-code, unless they are used within a set of SAMP-tags. You may
use quotes and amps in the text, but not in tags (such as the ALT-text of an IMG-tag). These letters are:-
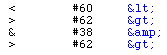
Also the non-breaking space entity is useful, since the browser normally won't care about multiple spaces, while multiple non-breaking spaces can be used as a simple way to add some horizontal space.
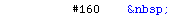
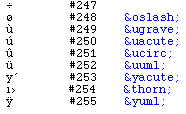
Other Special Characters
Some of these characters cannot be printed in Courier, which is used here, or in Times
that is the standard www-font. If you need characters that doesn't appear correctly,
make it as a picture instead.